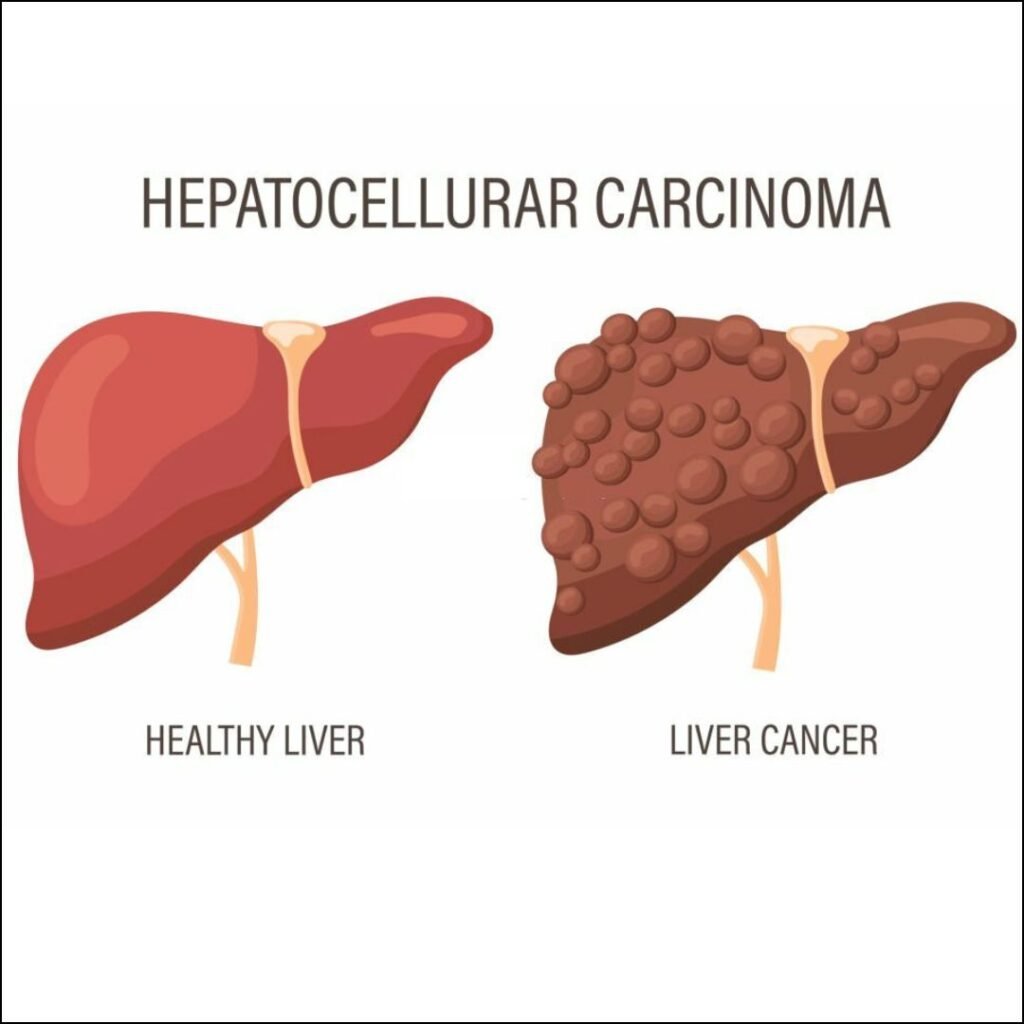
Hepatic Adenoma (Liver Adenoma
Hepatic Adenoma is a rare benign (non-cancerous) liver tumor.
It is more common in women, especially those using oral contraceptives.
Most cases have no symptoms and are found during imaging tests.
Large adenomas may cause pain or risk of bleeding.
Surgery is considered if the tumor is big or at risk of complications.
Hepatic Adenoma (Liver Adenoma Read Post »