Upper vs Lower UTI
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are classified into upper and lower types.
Lower UTI affects the bladder (cystitis) and urethra, causing burning urination, urgency, and pelvic pain.
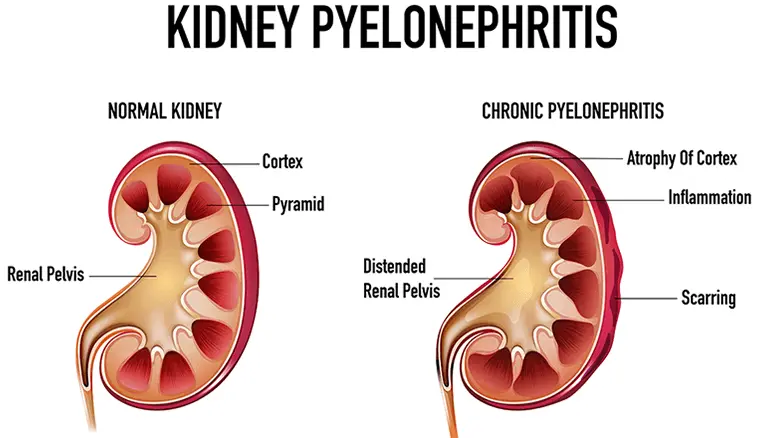
Upper UTI involves the kidneys (pyelonephritis), with fever, chills, nausea, and flank pain.
Upper UTIs are more serious and can lead to kidney damage or sepsis if untreated.
Early recognition and proper treatment help prevent complications in both types.
Upper vs Lower UTI Read Post »