Colon Cancer (Large Intestine Cancer)
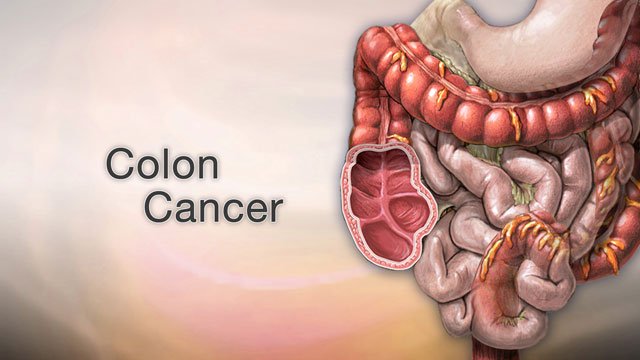
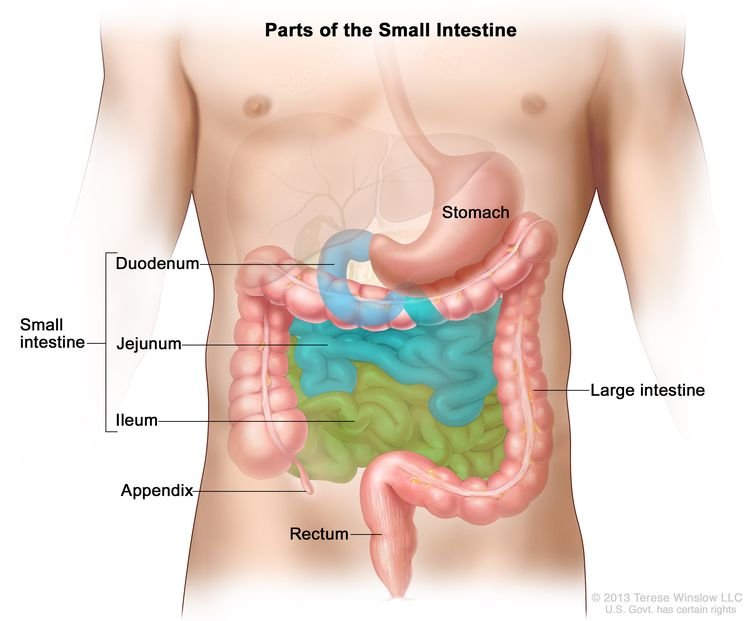
Colon Cancer, also called Large Intestine Cancer, begins in the colon, the longest part of the large intestine.
It usually develops from precancerous polyps that gradually turn cancerous over time.
Risk factors include older age, family history, obesity, low-fiber diet, smoking, and alcohol use.
Symptoms include changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, abdominal pain, weakness, and weight loss.
Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
Colon Cancer (Large Intestine Cancer) Read Post »