Folliculitis (Inflammation of Hair Follicles)
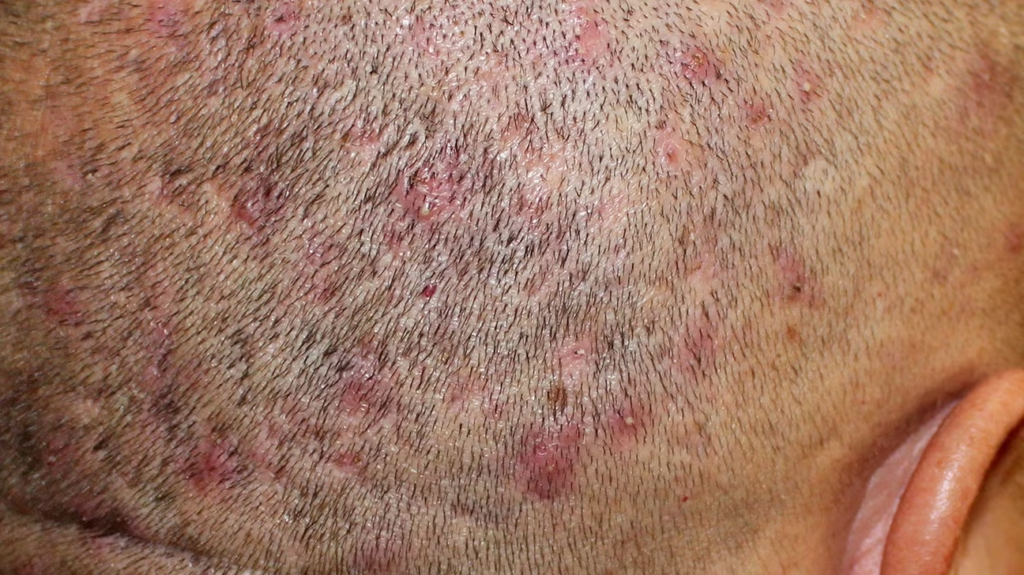
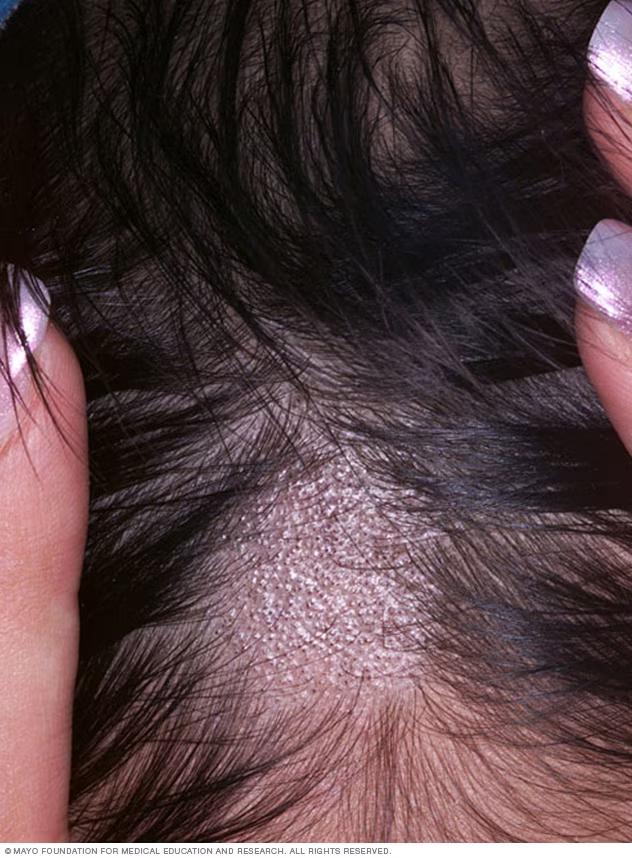
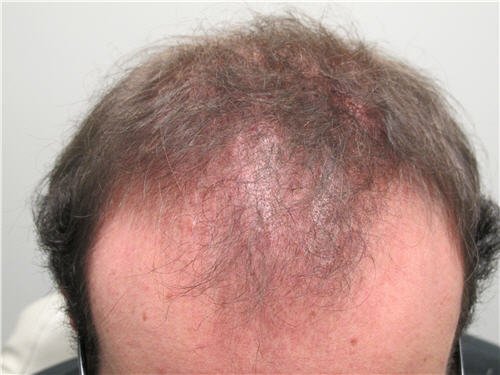
Folliculitis is the inflammation or infection of hair follicles, often caused by bacteria, fungi, or irritation.
It commonly appears as small red bumps or pustules resembling pimples around hair roots.
Symptoms include itching, pain, tenderness, and sometimes pus-filled blisters.
Risk factors include shaving, sweating, tight clothing, or weakened immunity.
Treatment involves topical or oral antibiotics/antifungals, warm compresses, and good hygiene.
Folliculitis (Inflammation of Hair Follicles) Read Post »