Neurogenic (Neurological) Constipation
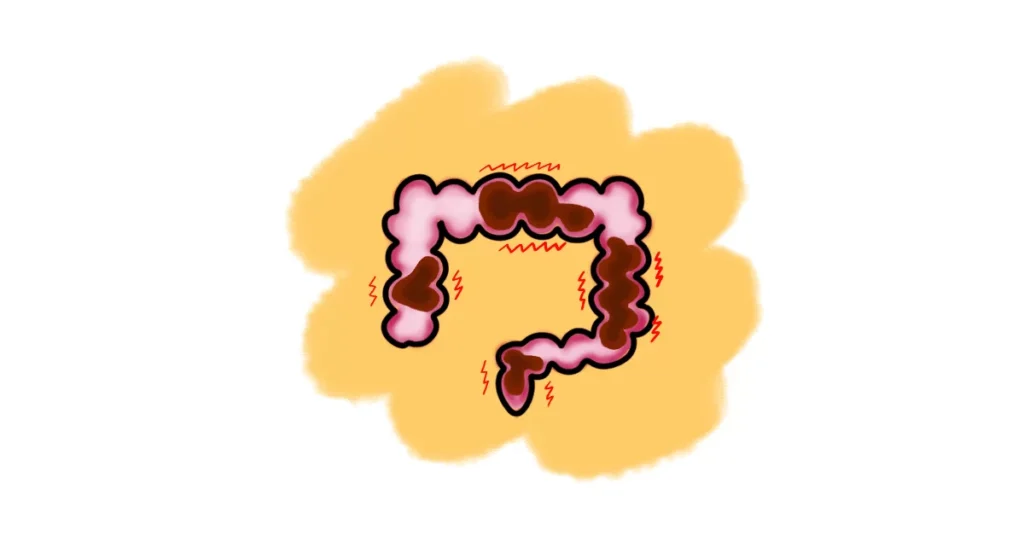
Neurogenic Constipation occurs when nerve-related disorders interfere with normal bowel movement control.
It is commonly seen in conditions like spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or stroke.
Patients experience infrequent stools, straining, bloating, and incomplete evacuation due to poor nerve signaling.
The problem arises from disrupted communication between the brain, spinal cord, and intestinal muscles.
Management includes bowel training, dietary changes, medications, and sometimes electrical or physical stimulation therapies.
Neurogenic (Neurological) Constipation Read Post »