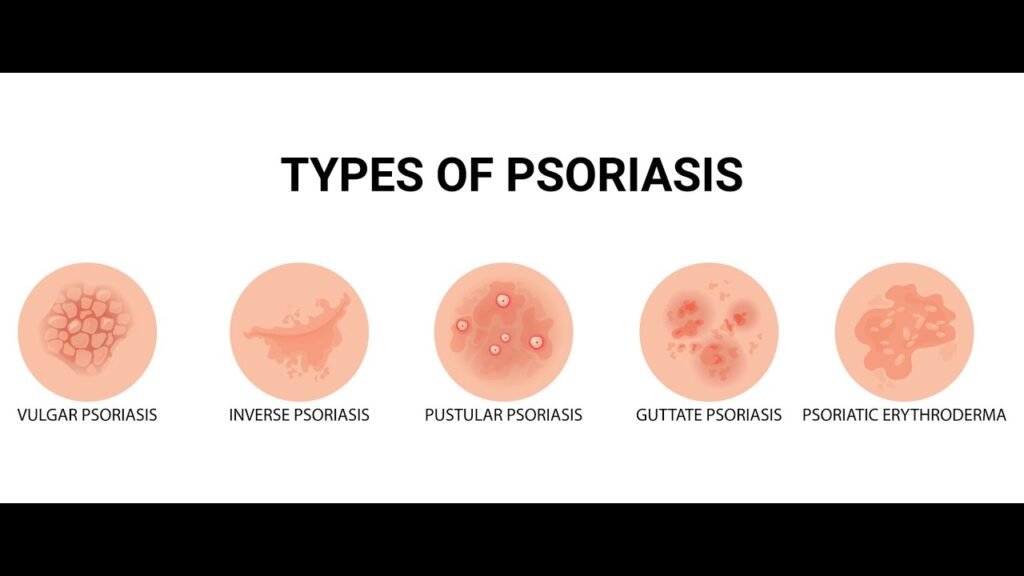
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
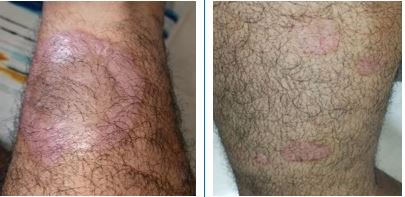
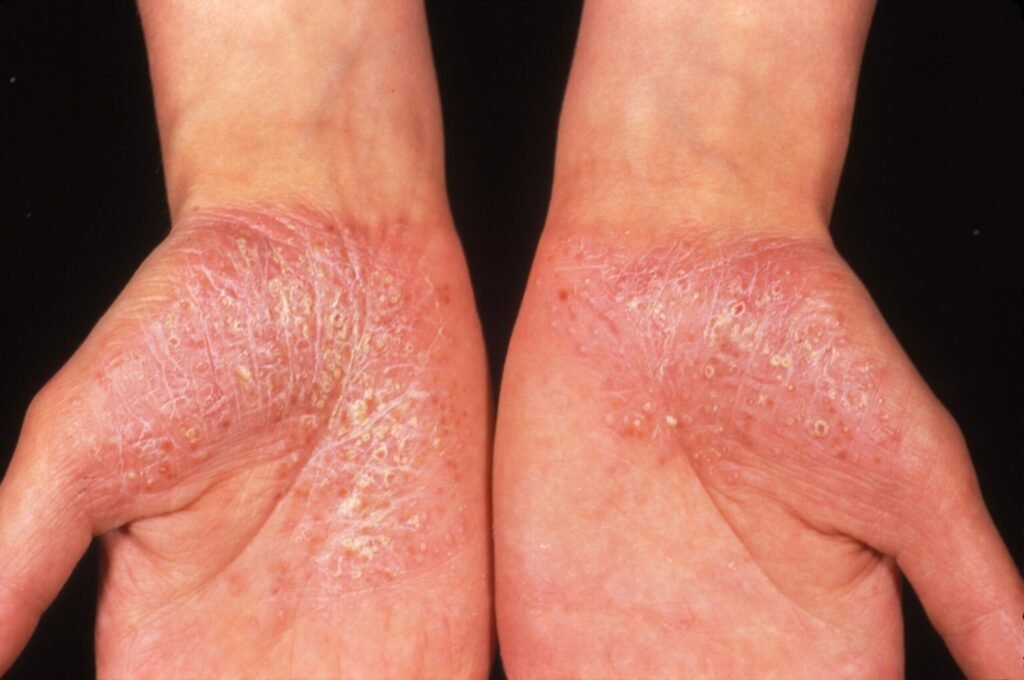
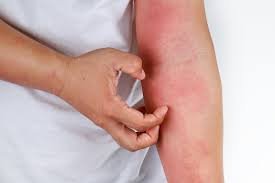
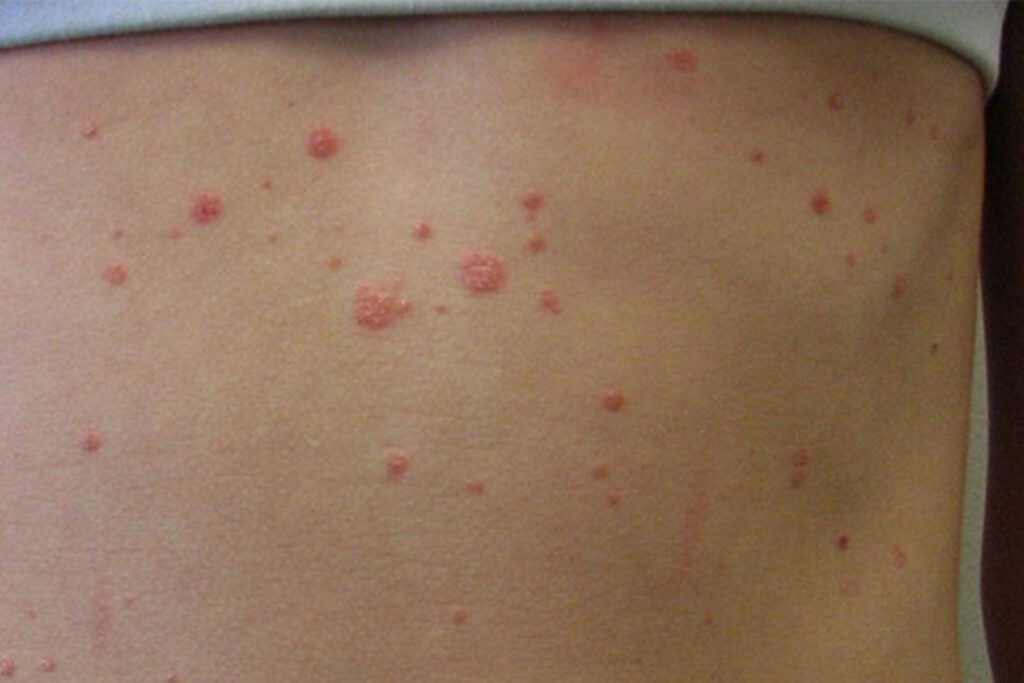
Erythrodermic Psoriasis is a rare, severe form of psoriasis involving widespread redness, scaling, and inflammation of most of the body’s surface. It can be life-threatening due to fluid loss, infection, or temperature imbalance. In homeopathy, treatment focuses on restoring immune balance and reducing systemic inflammation. Remedies like Arsenicum Album, Sulphur, and Rhus Toxicodendron are often considered based on symptoms. Early intervention and holistic management are crucial for recovery and prevention of relapses.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis Read Post »