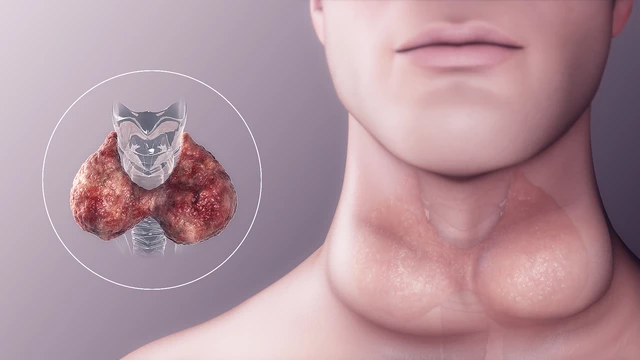
Congenital Hypothyroidism
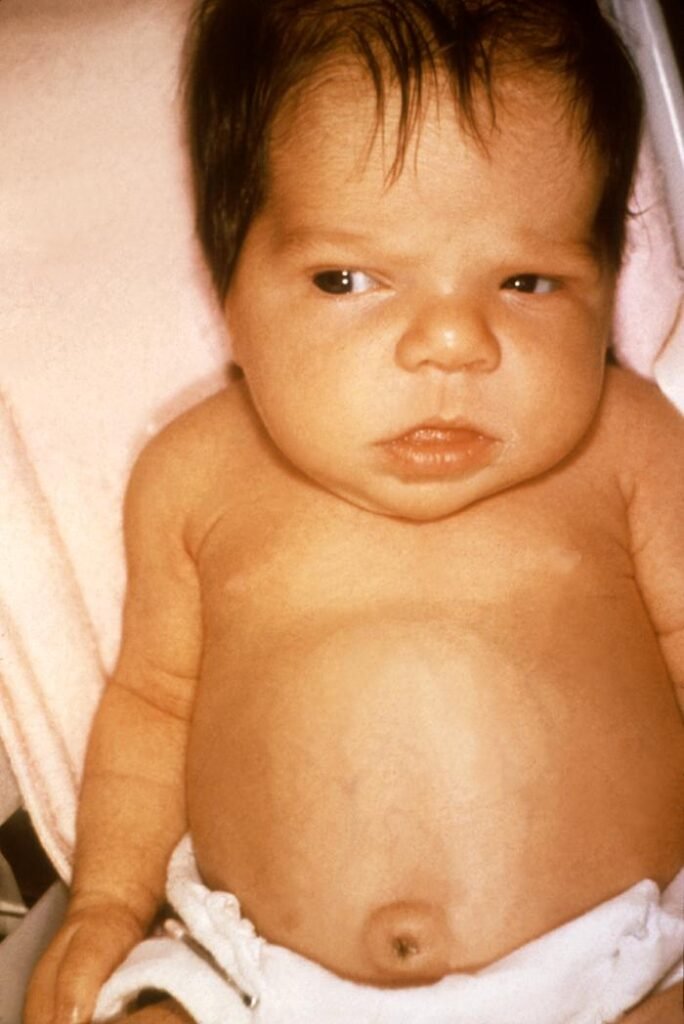
Congenital hypothyroidism is a condition present at birth due to an underactive or absent thyroid gland.
It can result from genetic defects, iodine deficiency, or developmental abnormalities of the thyroid.
Early symptoms include prolonged jaundice, poor feeding, lethargy, and delayed growth.
If left untreated, it can lead to intellectual disability and growth retardation.
Early detection through newborn screening and prompt thyroid hormone therapy ensure normal development.
Congenital Hypothyroidism Read Post »