नॉन-अल्कोहलिक फैटी लिवर डिजीज (NAFLD)
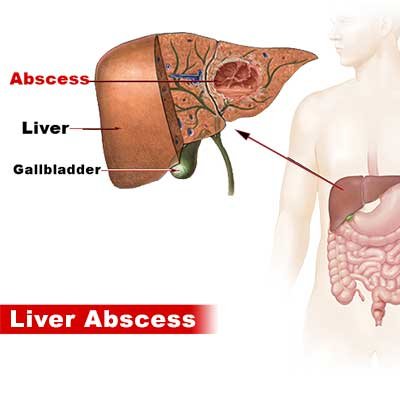
NAFLD is a common liver condition in which excess fat builds up in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. It is closely linked with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and sedentary lifestyle. In its early stages, NAFLD often causes no symptoms, but it can progress to inflammation (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Common signs may include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and enlarged liver. Management mainly involves weight loss, healthy diet, regular exercise, and control of diabetes and cholesterol. Early lifestyle changes can prevent complications and improve liver health.
नॉन-अल्कोहलिक फैटी लिवर डिजीज (NAFLD) Read Post »