Graves’ Disease
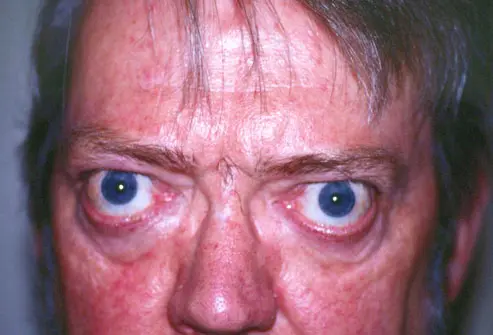
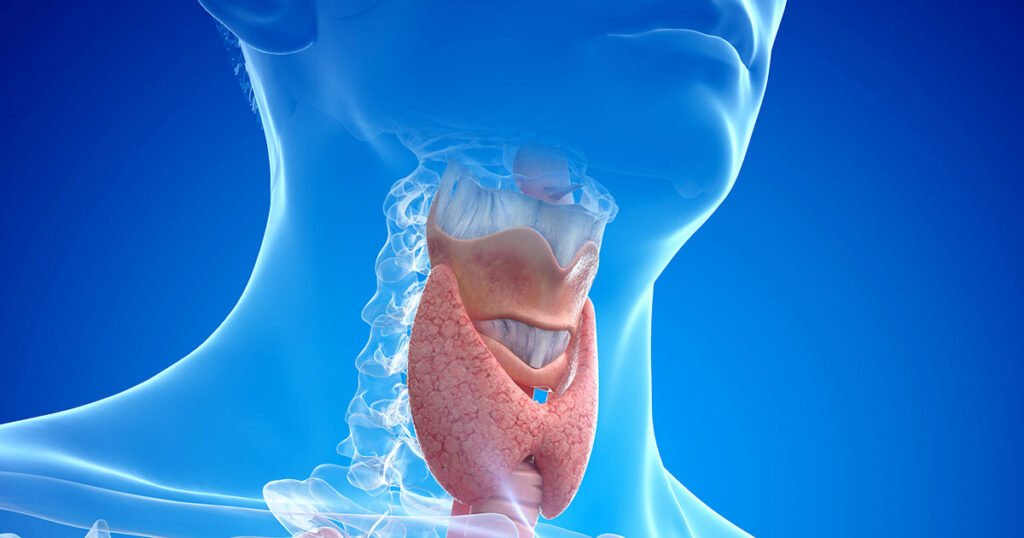
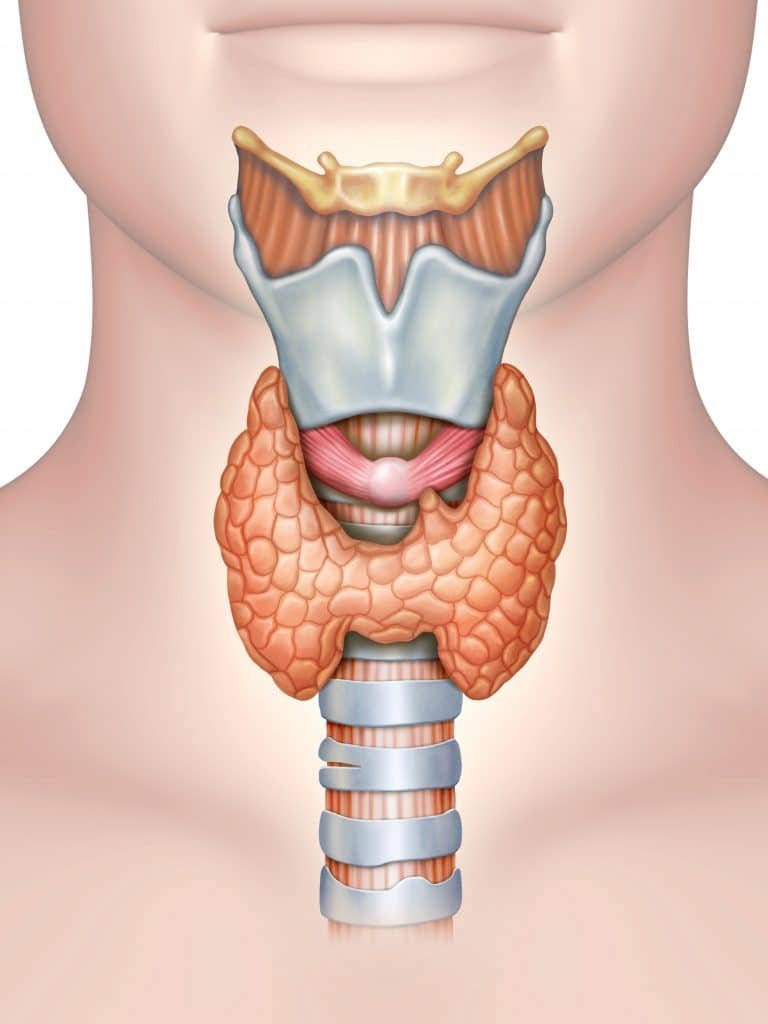
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to overproduce thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism).
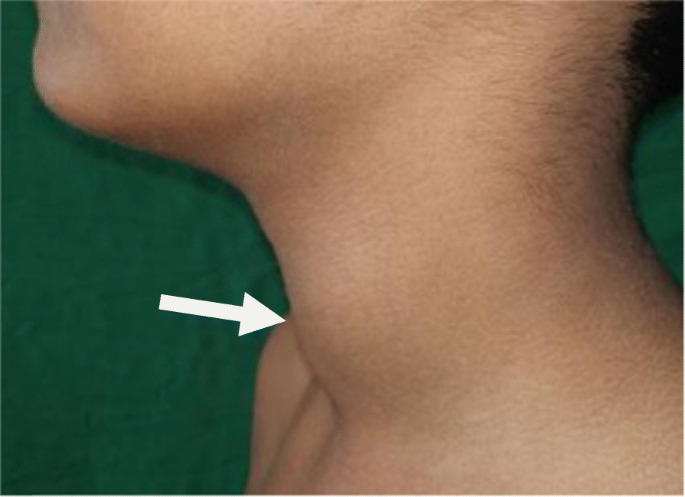
It is more common in women and often associated with goiter and eye symptoms like bulging eyes (exophthalmos).
The condition leads to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and heat intolerance.
It results from antibodies stimulating the thyroid to produce excess hormones.
Early diagnosis and proper management can prevent severe complications and improve quality of life.