Thyroid Carcinoma
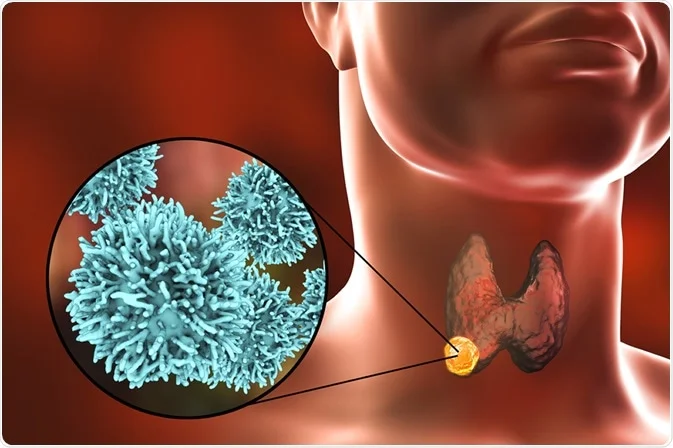
Thyroid carcinoma is a malignant tumor originating from the thyroid gland’s epithelial cells.
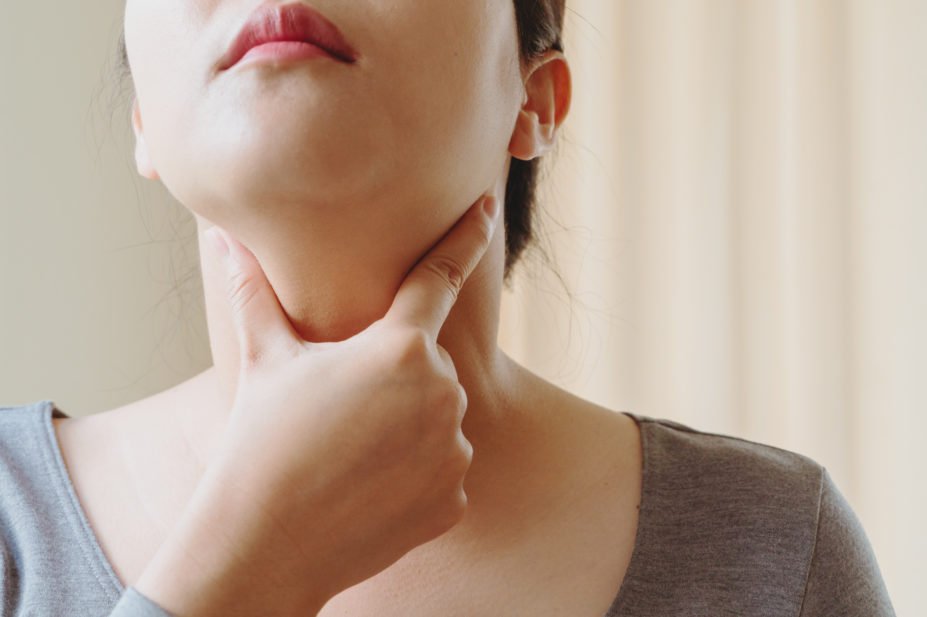
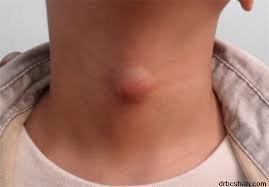
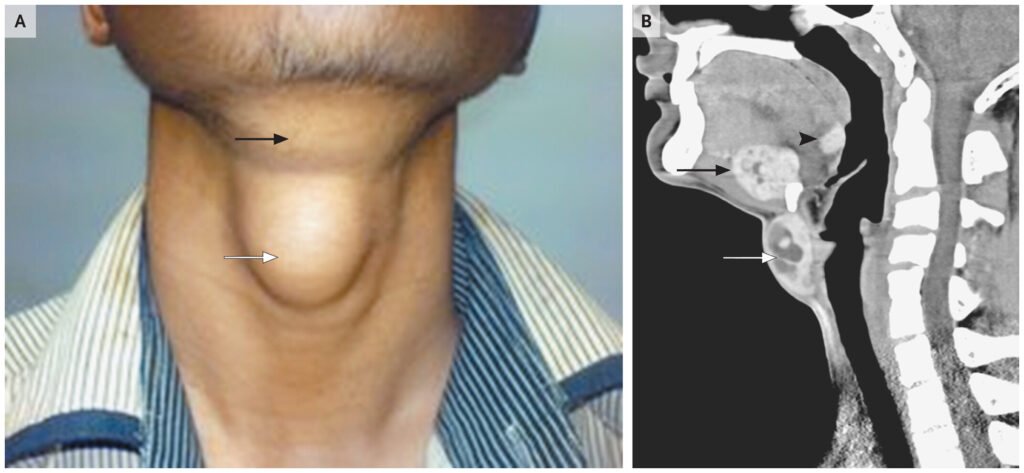
It may present as a painless neck nodule, sometimes associated with hoarseness or swallowing difficulty.
The major types include papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic carcinoma.
Early detection through ultrasound and biopsy improves prognosis significantly.
Treatment usually involves surgery, radioactive iodine, and lifelong thyroid hormone therapy.