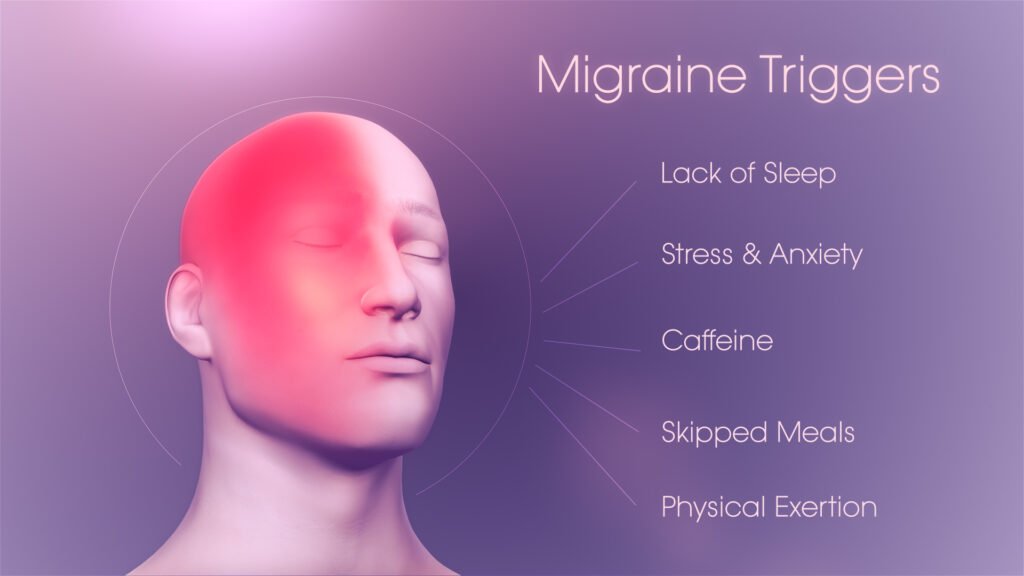
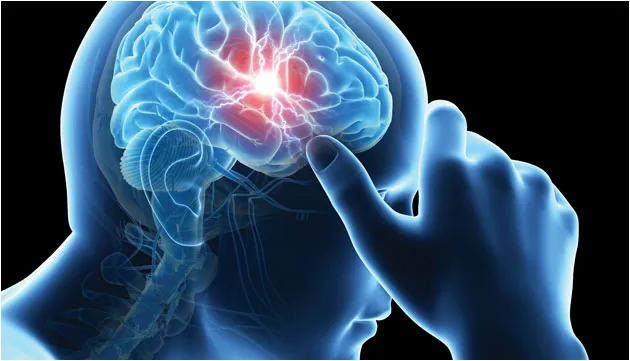
Stress-Induced Migraine
Stress-Induced Migraine is triggered by emotional or physical stress.
It causes throbbing head pain, sensitivity to light, and nausea.
Tension, anxiety, or overwork can lead to an attack.
Managing stress through relaxation and rest helps reduce episodes.
Treatment includes lifestyle changes and prescribed medication.
Stress-Induced Migraine Read Post »