Chronic Liver Failure (CLF)
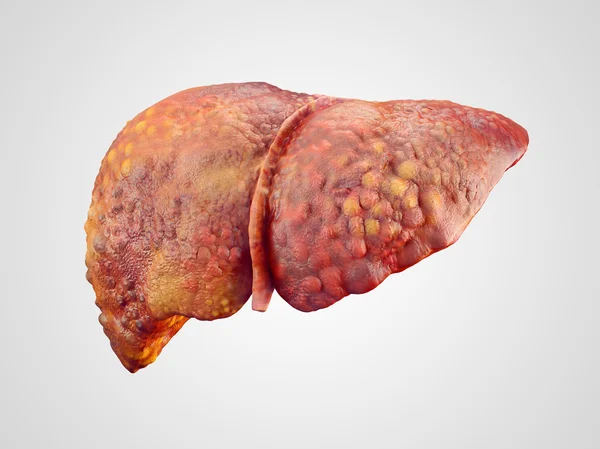
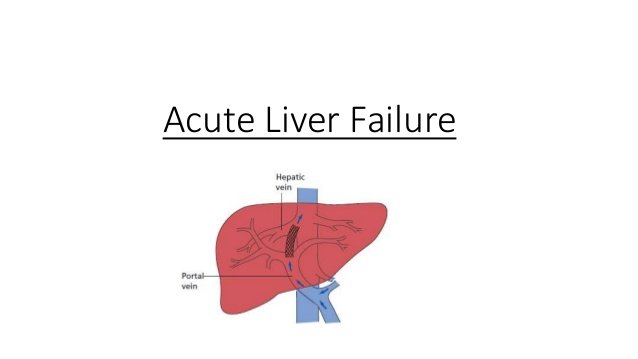
Chronic Liver Failure (CLF), also called end-stage liver disease, develops gradually over months to years due to long-term liver damage.
The most common causes include chronic hepatitis infections, alcohol abuse, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis.
Symptoms often include jaundice, abdominal swelling (ascites), easy bruising or bleeding, fatigue, and confusion (hepatic encephalopathy).
It is a progressive and serious condition, where the liver gradually loses its ability to function.
Management includes lifestyle changes, medications, treating underlying cause, and in advanced cases, liver transplantation may be required.
Chronic Liver Failure (CLF) Read Post »