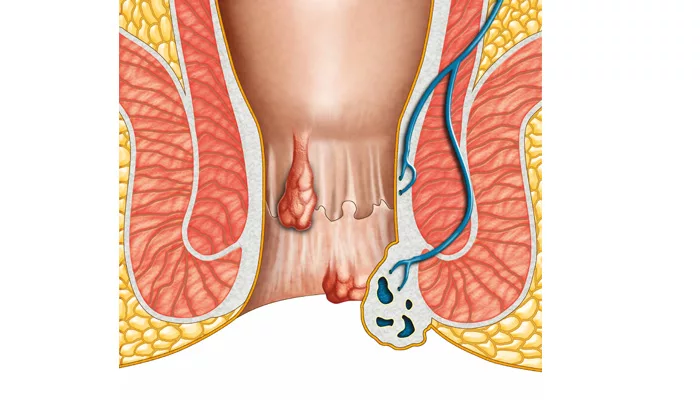
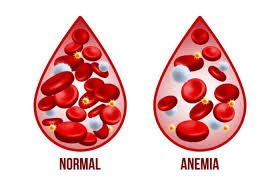
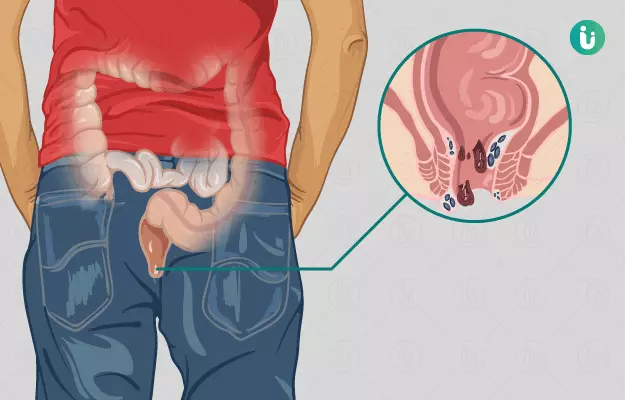
Complications of Piles (Hemorrhoids)
Untreated piles can lead to complications such as persistent pain, itching, and swelling.
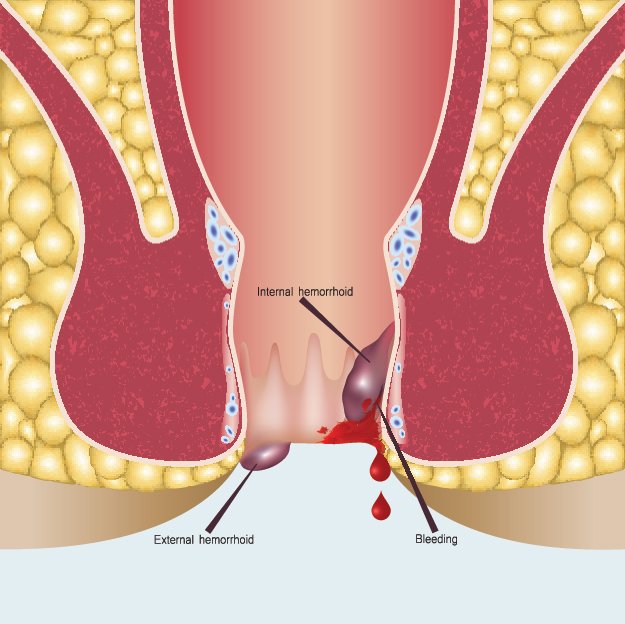
Bleeding piles may cause anemia if blood loss is frequent and significant.
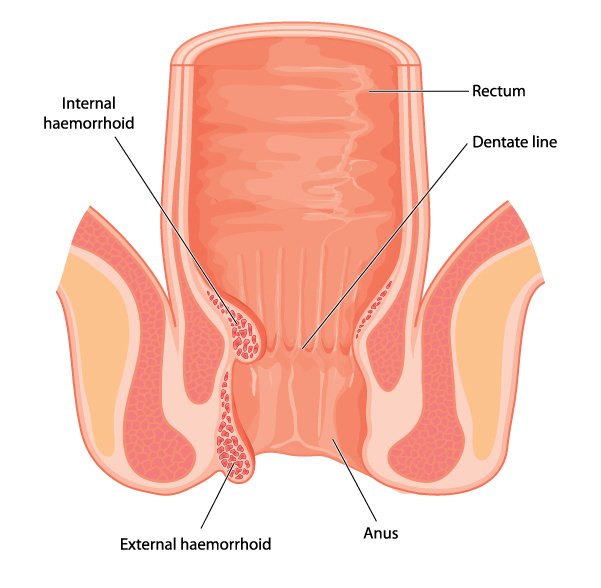
Prolapsed or thrombosed hemorrhoids can result in severe pain, clot formation, and infection.
Chronic inflammation may lead to skin irritation, ulcers, or difficulty maintaining hygiene.
In advanced cases, surgery may be required to prevent worsening and restore quality of life.
Complications of Piles (Hemorrhoids) Read Post »