Pregnancy & Postpartum Constipation
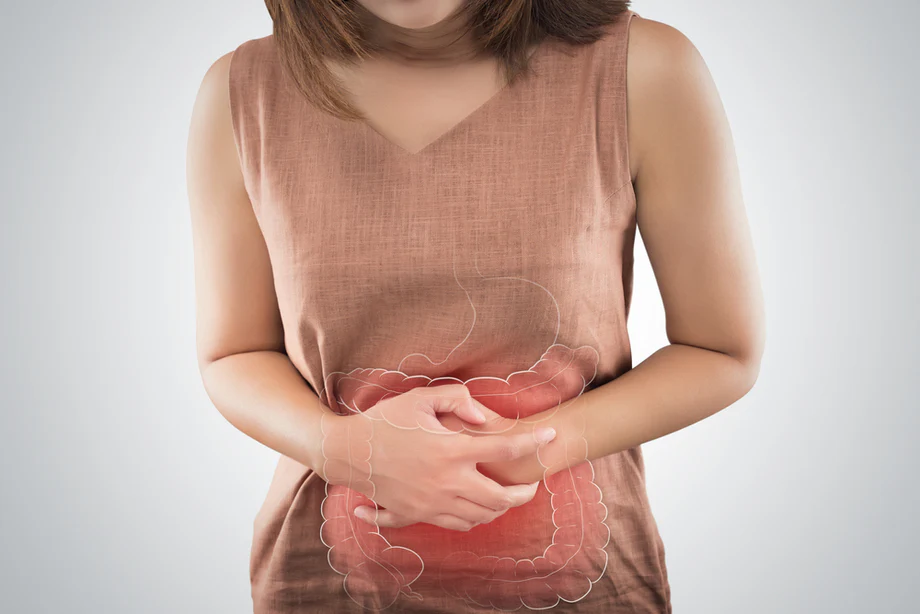
Pregnancy & Postpartum Constipation is common due to hormonal changes, pressure from the growing uterus, and reduced physical activity.
Iron supplements and dietary changes during pregnancy may further worsen constipation.
Symptoms include hard stools, bloating, abdominal discomfort, and straining.
After delivery, constipation may persist due to weakened pelvic floor muscles or post-surgical effects.
Management includes high-fiber diet, hydration, gentle exercise, and safe laxatives under medical guidance.
Pregnancy & Postpartum Constipation Read Post »