Gestational Diabetes
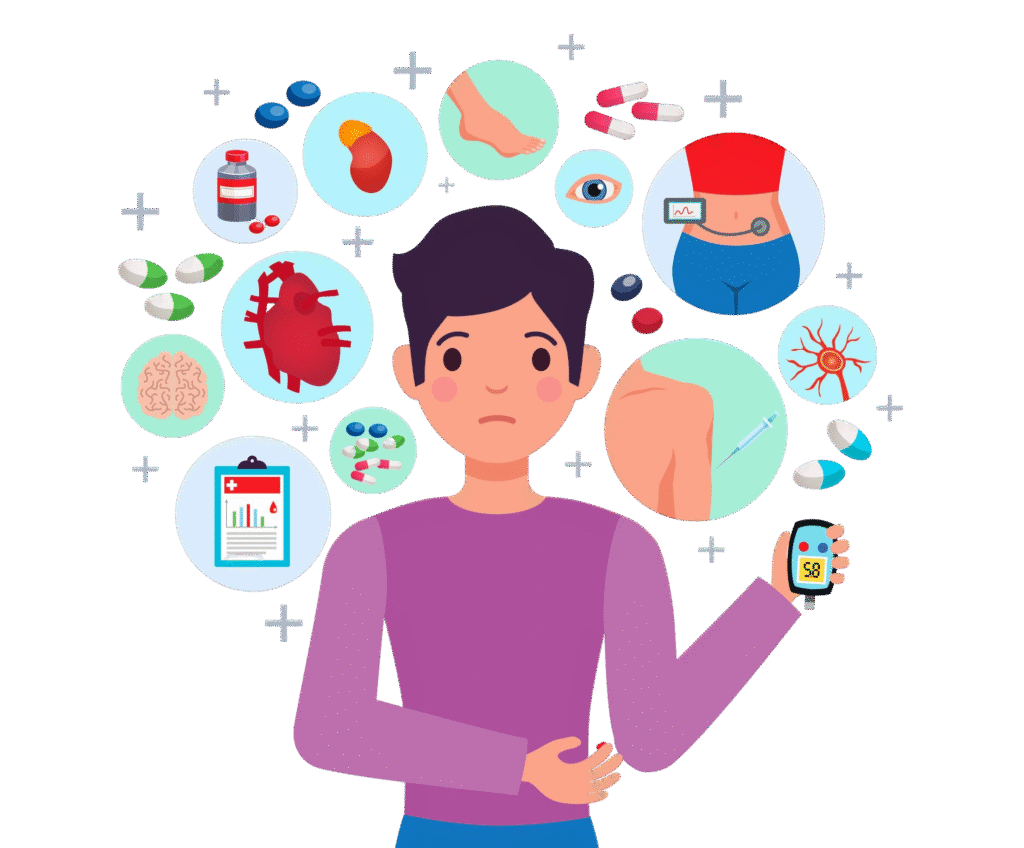
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet increased demands. This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can affect both the mother and the baby. Risk factors include obesity, a family history of diabetes, advanced maternal age, and previous pregnancy complications. While gestational diabetes often resolves after delivery, it increases the risk of high birth weight, premature delivery, and cesarean section. Mothers are also at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Careful blood sugar monitoring, healthy eating, regular exercise, and in some cases insulin therapy are important for managing gestational diabetes and ensuring a safe pregnancy outcome.
Gestational Diabetes Read Post »