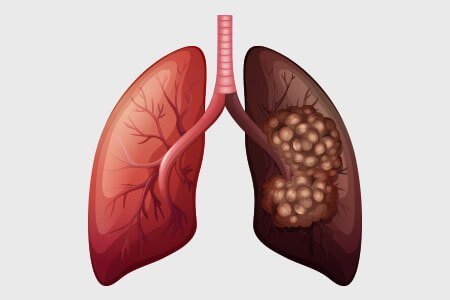
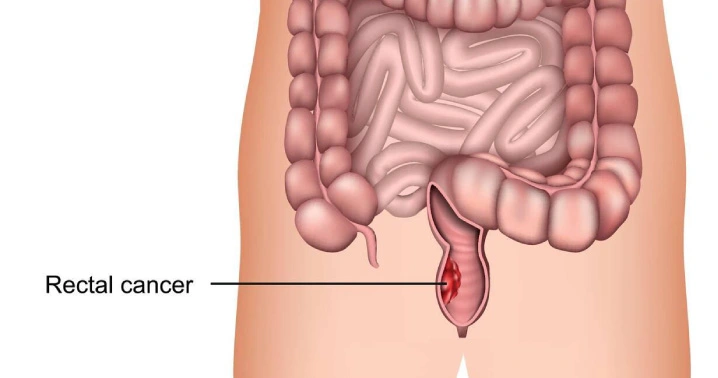
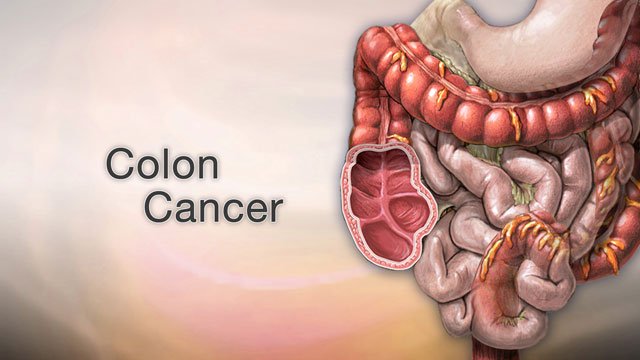
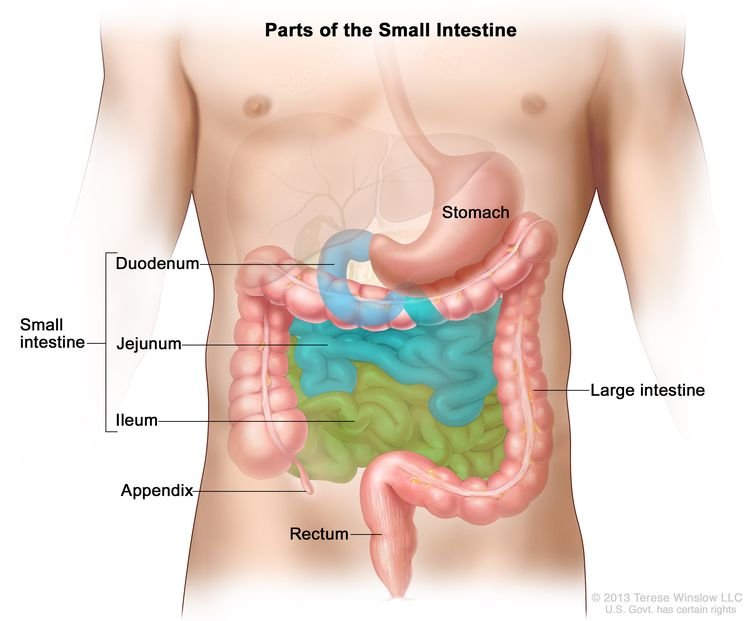
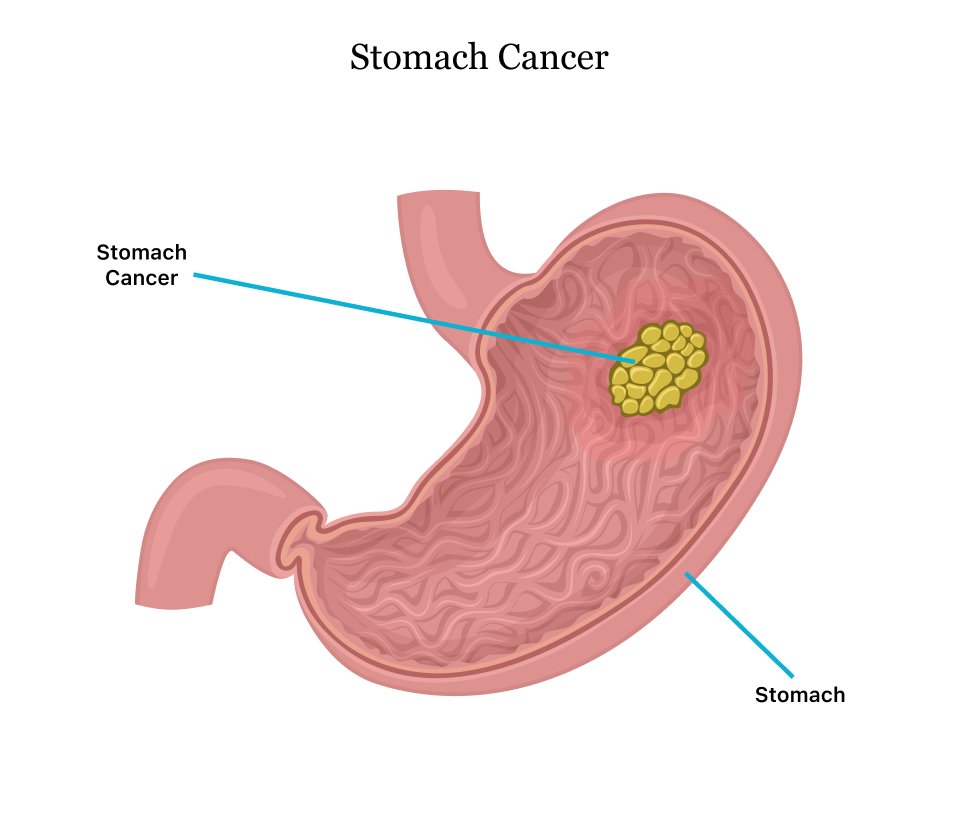
Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lungs, interfering with breathing.
It is strongly associated with smoking, but can also occur due to pollution, asbestos, and genetic factors.
The two main types are small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and weight loss.
Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.