What is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is the amount of glucose present in your blood at any given time.
Glucose is the main type of sugar that comes from the food you eat — especially carbohydrates like rice, bread, fruits, and sweets.
It is the body’s primary source of energy for muscles, brain, and other organs.
How Does Blood Sugar Work in the Body
- After you eat, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which enters your blood.
- Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps glucose move from the blood into the cells, where it’s used for energy.
- Between meals, your liver stores extra glucose as glycogen and releases it when your blood sugar drops.
- This balance keeps your body functioning normally.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
- (Fasting = before eating anything in the morning, Post-meal = 2 hours after eating)
- Fasting: 70 – 99 mg/dL (normal)
- Post-meal: Less than 140 mg/dL (normal)
- Prediabetes: Fasting 100 – 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: Fasting 126 mg/dL or higher, confirmed on two separate tests.
When Blood Sugar is Too High (Hyperglycemia)
- Causes: Diabetes, stress, infections, overeating sweets, certain medicines.
- Symptoms: Excessive thirst, frequent urination, tiredness, blurred vision, slow healing of wounds.
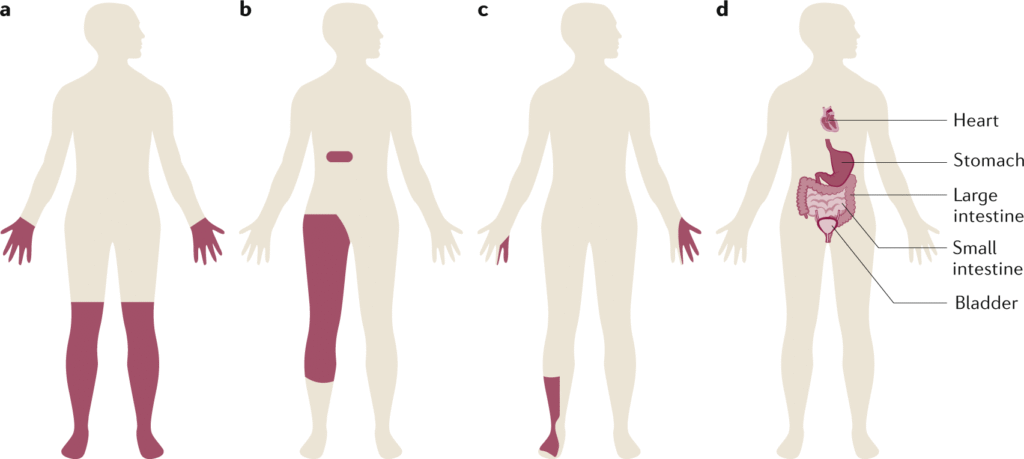
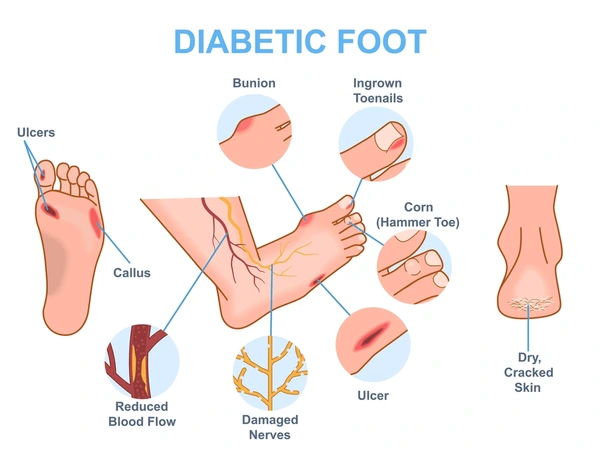
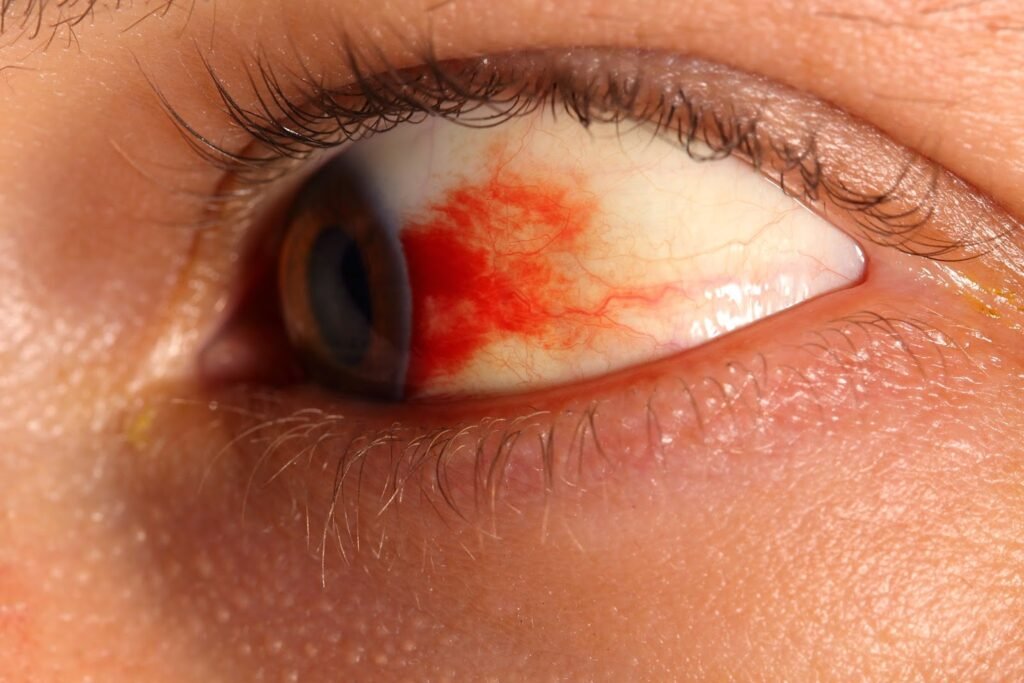
- Long-term risk: Damage to heart, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
When Blood Sugar is Too Low (Hypoglycemia)
- Causes: Too much insulin/diabetes medicines, skipping meals, heavy exercise without eating, alcohol.
- Symptoms: Sweating, shakiness, fast heartbeat, confusion, headache, fainting.
- Severe cases: Can lead to seizures or coma.
Why is Blood Sugar Important
- Maintaining normal blood sugar is vital for energy supply and preventing organ damage.
- Both high and low blood sugar can be dangerous if not managed promptly.
Relatated blood sugar problems
Blood Sugar Problems (High, Low & Prediabetes)
Blood sugar problems are the most directly connected conditions to diabetes.
When we eat food — especially carbohydrates like rice, bread, sweets — the body breaks it down into glucose (sugar) for energy. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps move this glucose from blood into cells.
If insulin doesn’t work properly or isn’t enough, sugar stays in the blood — leading to high blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
Types of Blood Sugar Problems:
1. Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
- Blood glucose level is higher than normal.
- Common in untreated diabetes or poorly managed diabetes.
- Symptoms: Frequent urination, excessive thirst, tiredness, blurred vision, slow wound healing.
2 . Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
- Blood glucose drops too low (usually <70 mg/dL).
- Can happen in diabetics who take too much insulin/medicine, skip meals, or exercise heavily without adjusting food/meds.
- Symptoms: Sweating, trembling, hunger, confusion, dizziness, in severe cases fainting or seizures.
3. Prediabetes
- Blood sugar higher than normal but not yet diabetes (fasting sugar 100–125 mg/dL).
- Warning stage — many people don’t know they have it.
- Lifestyle changes at this stage can prevent Type 2 diabetes.
4. Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT)
- Similar to prediabetes, but diagnosed with a sugar tolerance test.
- Shows that the body is struggling to manage sugar after meals.
Why it’s linked to diabetes:
- Blood sugar imbalance is the core of diabetes — every diabetic has either too high sugar (chronic) or sometimes too low sugar (if overtreated).Prediabetes and IGT are warning signs for future diabetes.
Homeopathic View:
Homeopathy aims to improve the body’s natural insulin efficiency, reduce fluctuations in blood sugar, and prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes with proper remedies, diet, and lifestyle guidance.