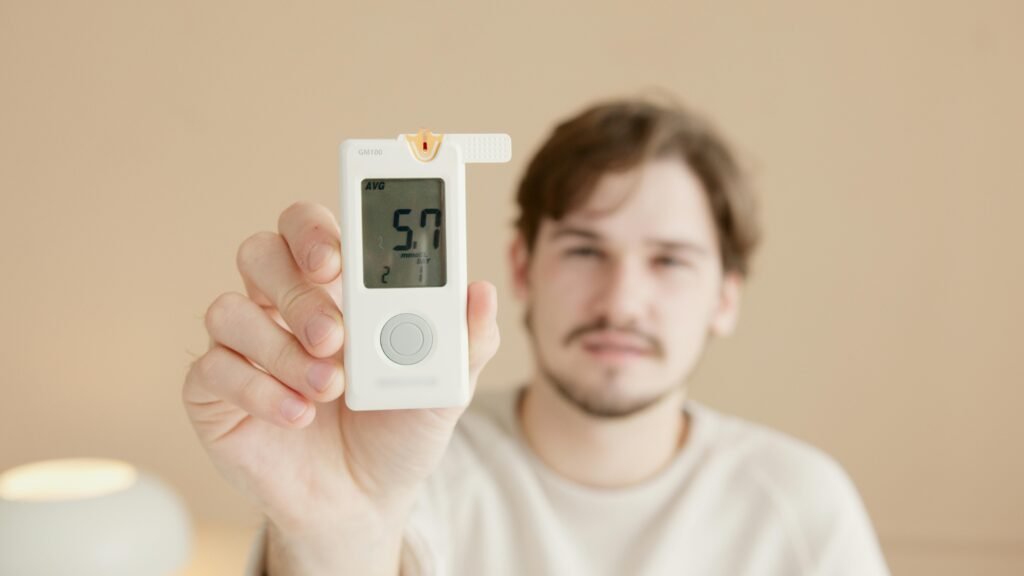
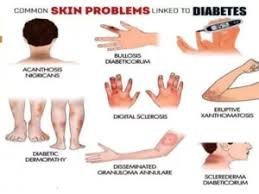
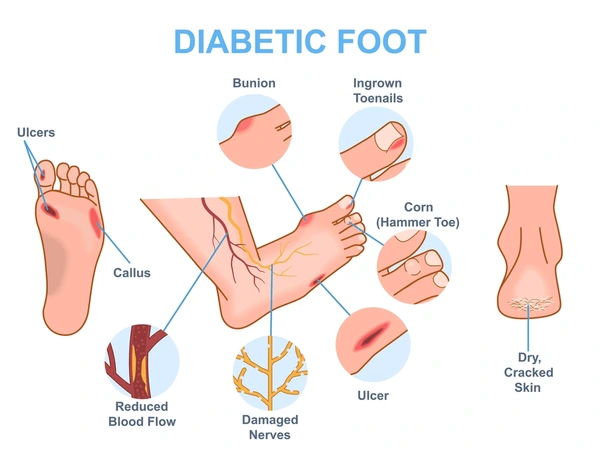
Skin Conditions Related to Diabetes
Skin conditions related to diabetes are common and may include dryness, itching, dark patches, bacterial or fungal infections, and slow-healing sores, often linked to poor blood circulation and high blood sugar.
Skin Conditions Related to Diabetes Read Post »