Diabetes & Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
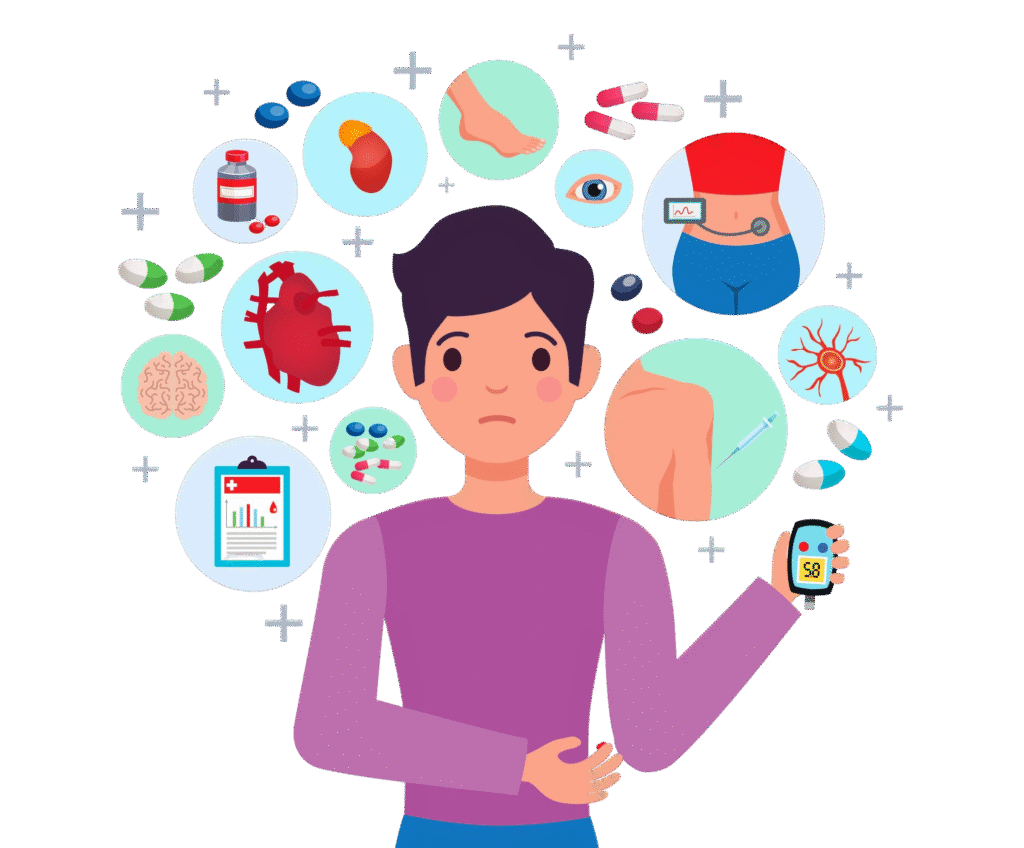
Diabetes and hypertension often occur together, and their combination greatly increases the risk of serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and vision problems. High blood sugar damages blood vessels and nerves, while high blood pressure puts extra strain on the cardiovascular system, accelerating the progression of complications. Managing both conditions through regular monitoring, healthy diet, reduced salt intake, physical activity, stress control, and prescribed medications is essential to protect long-term health and reduce risks.
Diabetes & Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Read Post »