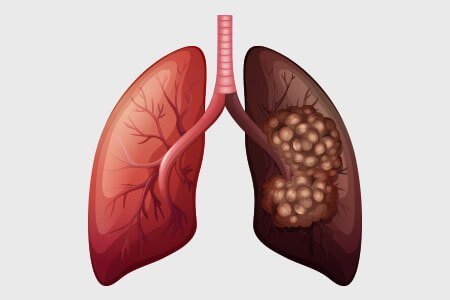
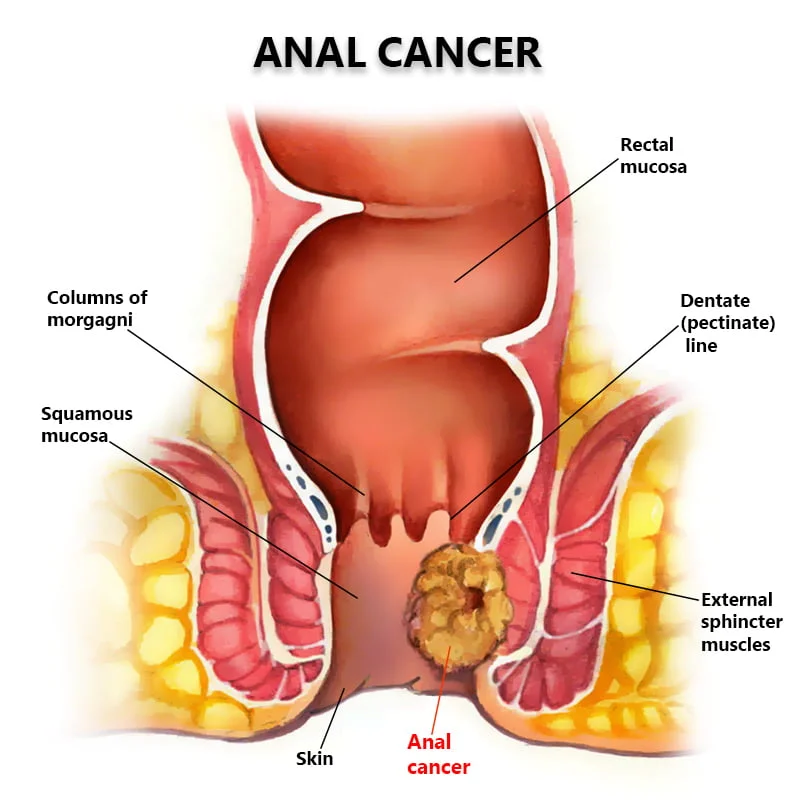
Uterine Cancer (Endometrial Cancer)
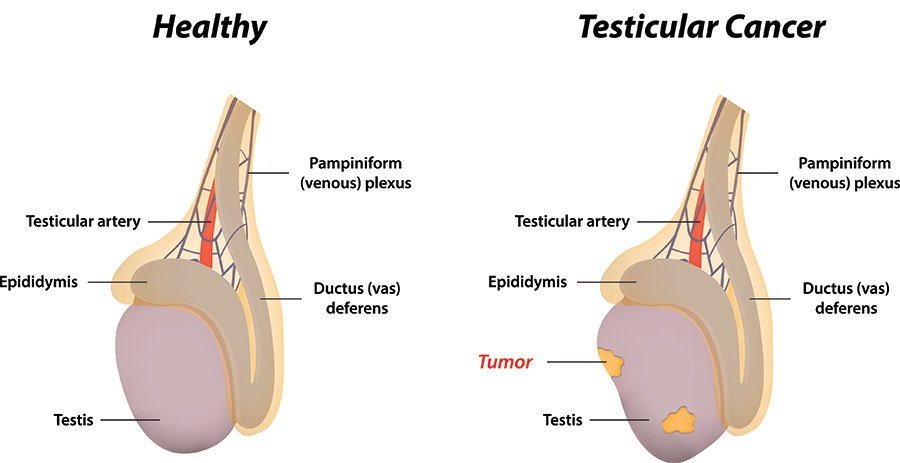
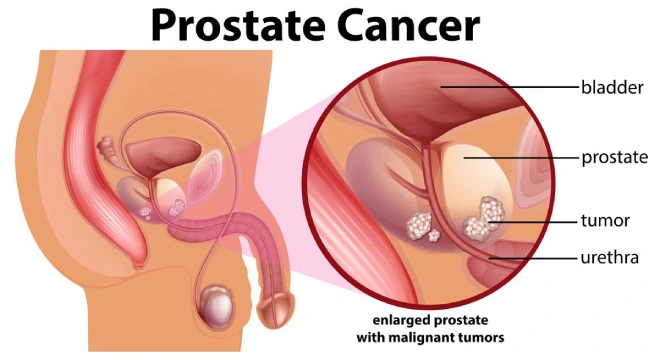
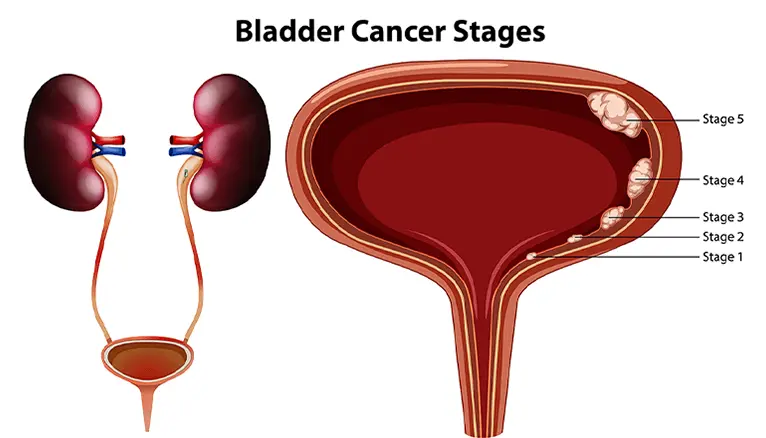
Uterine Cancer, most commonly Endometrial Cancer, develops in the lining of the uterus (womb).
It is more common in postmenopausal women and linked to obesity, hormonal imbalance, and family history.
Symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, painful urination, and pain during intercourse.
If untreated, it can spread to nearby pelvic organs and lymph nodes.
Treatment may include surgery (hysterectomy), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted therapy.
Uterine Cancer (Endometrial Cancer) Read Post »