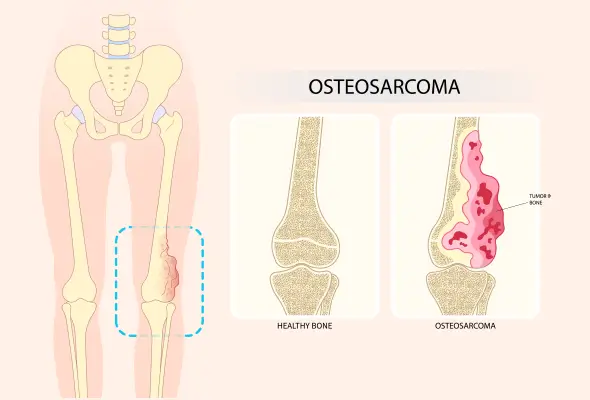
Ewing’s Sarcoma
Ewing’s Sarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that usually starts in the bones or soft tissue around them.
It mainly affects children, teenagers, and young adults, with the pelvis, thigh bones, and ribs being common sites.
Symptoms include bone pain, swelling, tenderness, fever, fatigue, and occasional fractures.
The exact cause is unclear, but it is often linked to genetic mutations and abnormal cell growth.
Treatment involves a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes targeted therapy.