Multinodular Goitre (MNG)
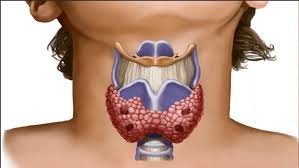
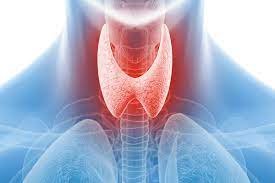
Multinodular goitre (MNG) is a condition in which the thyroid gland develops multiple nodules.
It often results from long-standing iodine deficiency or genetic factors.
Symptoms may include visible neck swelling, difficulty swallowing, and, in some cases, hyperthyroidism.
The nodules can be benign, but some may rarely become cancerous.
Treatment depends on the size, symptoms, and thyroid function, and may include observation, medications, or surgery.
Multinodular Goitre (MNG) Read Post »