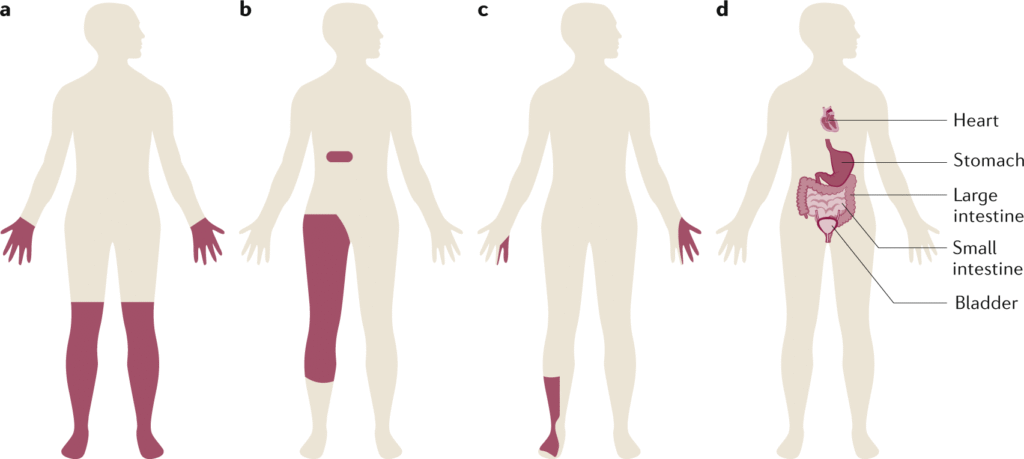
What is Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) metabolic disorder in which the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. Glucose is the main source of energy for our body’s cells, and insulin (a hormone produced by the pancreas) helps glucose enter the cells.
In diabetes, either the body does not produce enough insulin or the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin (insulin resistance), leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
Understanding Diabetes in Homeopathy
- In modern medicine, diabetes is a metabolic disorder due to insulin deficiency/resistance.
- In homeopathy, it is seen as a chronic miasmatic disease (deep-seated constitutional disturbance).
- It is not just about sugar levels, but about deranged vitality (वाइटल फोर्स की गड़बड़ी).
Causes (from Homeopathic philosophy)
- Heredity (genetic) – Often a strong family history (psoric-sycotic influence).
- Suppressed diseases – Skin eruptions, gonorrhea, syphilis when suppressed → internal disease develops.
- Lifestyle factors – Stress, excess alcohol, sedentary life.
- Constitutional weakness – Nervous system and pancreatic function deranged.
Symptoms
Not only:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Weight loss
But also:
- Mental symptoms (irritability, depression, anxiety about future)
- Food cravings (sweets, cold drinks, alcohol, spicy food)
- Thermal state (chilly vs hot patient)
- Modalities (what makes patient better/worse)
- Family history (TB, cancer, diabetes, mental illness).
Types of Diabetes
A. Diabetes Mellitus
- The most common form, which is further divided into:
Type 1 Diabetes
- Autoimmune condition: the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Usually develops in childhood or young adulthood.
- Patients require lifelong insulin injections.
Type 2 Diabetes
- The body produces insulin but cells don’t respond to it effectively (insulin resistance).
- Often linked to obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors.
- Can be controlled with diet, exercise, medication, and sometimes insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes
- Develops during pregnancy in women who never had diabetes before.
- Usually disappears after childbirth but increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Other Specific Types
- Due to genetic defects, pancreatic diseases, hormonal disorders, or side effects of medicines.
B. Diabetes Insipidus (Not related to blood sugar)
- A rare disorder where the kidneys cannot conserve water properly.
- Caused by lack of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or kidney’s inability to respond to it.
- Main symptom: passing large amounts of dilute urine and extreme thirst.
3. Causes & Risk Factors
Type 1 Diabetes Causes:
- Autoimmune destruction of beta cells.
- Possible triggers: viral infections, genetic predisposition.
Type 2 Diabetes Causes:
- Insulin resistance.
- Overweight/obesity.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Unhealthy diet.
- Family history.
- Age over 40 (though now common in younger people too).
- Gestational Diabetes Causes:
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy causing insulin resistance.
- Diabetes Insipidus Causes:
- Damage to hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
- Kidney disorders.
- Certain medications.
Homeopathic Remedies Commonly Used in Diabetes
- (Selected according to symptoms, not disease name!)
- Syzygium jambolanum – Known for lowering sugar, excessive thirst, profuse urination.
- Phosphoric Acid – Diabetes from grief, mental strain, weakness, apathetic mood.
- Phosphorus – Nervous patients, excessive thirst for cold water, weakness, burning.
- Uranium Nitricum – Intense thirst, emaciation, skin ulcers, digestive complaints.
- Cephalandra Indica – Sugar in urine, great debility, constipation.
- Sulphur – Long-standing diabetes with skin troubles, burning soles, craving for sweets.
- Lycopodium – Weak digestion, impotency, premature ageing in diabetics.
- Natrium Sulphuricum – Diabetes after liver troubles; aggravated by damp weather.
Homeopathic Philosophy in Treatment
- Individualization is key – No two diabetics get the same remedy.
- Miasmatic background must be treated to prevent complications (neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy).
- Constitutional remedy helps restore balance → improves immunity, slows complications.
- Acute intercurrent remedies (like Syzygium jamb.) can be used to control sugar levels.
Role of Homeopathy Today
- Not a replacement for insulin in Type 1 diabetes.
- In Type 2 diabetes – helps in early stages, reduces complications, and improves overall health.
- Works best as supportive & holistic therapy alongside lifestyle modification.
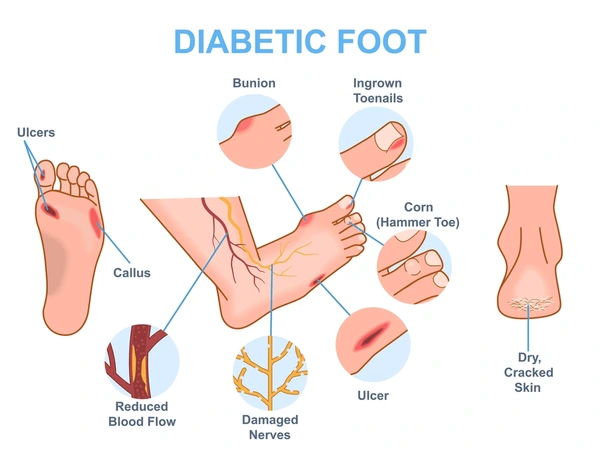
Complications (if uncontrolled)
- Individualization is key – No two diabetics get the same remedy.
- Miasmatic background must be treated to prevent complications (neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy).
- Constitutional remedy helps restore balance → improves immunity, slows complications.
- Acute intercurrent remedies (like Syzygium jamb.) can be used to control sugar levels.
Diagnosis
- Fasting Blood Sugar: ≥126 mg/dL
- Random Blood Sugar: ≥200 mg/dL with symptoms
- HbA1c: ≥6.5%
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: 2-hour value ≥200 mg/dL
Management & Treatment
Conventional Approach:
Type 1: Lifelong insulin therapy, balanced diet, regular exercise.
Type 2: Diet & exercise first, oral medications (e.g., metformin), insulin if needed.
- Gestational: Diet control, exercise, insulin if required.
- Insipidus: Treat cause, give desmopressin for ADH deficiency.
“Homeopathic Approach”:
Homeopathy does not simply “reduce sugar”; it aims to treat the patient as a whole, improve metabolism, and prevent complications. Commonly used remedies (chosen after case-taking):
- Syzygium jambolanum – Helps reduce sugar levels.
- Phosphoric acid – For debility and mental weakness from diabetes.
- Lycopodium – For digestive troubles and weakness in diabetics.
- Phosphorus – For complications like retinopathy.
- Arsenicum album – For burning pains and weakness.
- (Remedy selection should be individualized by a qualified homeopath.)
Lifestyle & Prevention
- Maintain healthy body weight.
- Eat balanced diet: high in fiber, low in refined carbs & sugars.
- Regular exercise (30 min/day).
- Avoid smoking & limit alcohol.
- Regular health check-ups.
- Regular health check-ups.
- Manage stress.